Make MCP Great (Again) - Enabling Analytics for Your TypeScript MCP Servers
To Vibe or Not To Vibe
"Vibe Coding" is on track to be the programmer's phrase of the year for 2025. The term, coined by Andrej Karpathy, describes a new way of coding largely with the help of LLMs, often in novel IDEs with AI integration such as Cursor or Windsurf.
Another term that is quickly rising in popularity is the Model Context Protocol (MCP). MCP is a new way of supplying your integrated LLM with various tools, enabling synchronous communication between external services within a prompt. It's like RAG on steroids. The programming world remains divided on whether MCP is a great innovation or just yet another new standard. I'll leave this judgment to you and let time tell. What I can say with certainty, though, is that the MCP ecosystem is evolving rapidly. New server implementations for all sorts of use cases are going viral every day.
After building my first MCP Server using the TypeScript SDK to scrape blockchain data from EVM blockchains, I felt the potential of this new trend but was simultaneously underwhelmed by the existing developer tooling. In this article, I outline my first step to improve this for the ecosystem by presenting mcp-analytics-middleware, a lightweight middleware based on SQLite that enables basic analytics for all requests on your MCP servers.
The Need For Better Dev Tools
Getting your first MCP Server to run within your IDE can be at least a little challenging. For most servers, however, it boils down to fetching an NPM package and running it either from source or via npx, providing the needed flags and environment variables. If this doesn't work, a first step for debugging your server implementation and its tools is using the inspector.
One thing I quickly realized was that I had no idea which tools my client was actually calling on the MCP Server. After enabling Auto-Run mode in Cursor settings, I discovered an API key had been exhausted because my LLM was spamming the respective MCP tools.
MCP Analytics Middleware
That's when I realized tooling is needed to provide the following functionality:
- See the number of requests for different tools
- Track durations and error logs of my MCP tools
- Rate limit my MCP (work in progress)
The result of this endeavor is MCP Analytics Middleware. It overrides the server implementation of the TypeScript SDK and injects a middleware that connects to a SQLite file specified by the user to track all resource and tool requests of the MCP Server.
How To Use It
Adding the middleware is as simple as installing the required mcp-analytics-middleware package:
yarn add mcp-analytics-middleware
Afterwards, you can use it with a few lines of code, overriding the default tool and request implementation of the MCP Server:
import { McpAnalytics } from 'mcp-analytics-middleware';
let server = new McpServer({
name: 'Sample MCP Server with Analytics',
version: '1.0.0'
});
const analytics = new McpAnalytics('analytics.db'); // specify path of SQLite database
server = analytics.enhance(server);
The GitHub Repository lists several sample implementations.
Demo
The following demo shows an example usage of the analytics middleware with the Google Maps MCP Server. We ask the LLM a question that requires different types of geographical information such as elevation and directions between locations. This information is retrievable through the following tools of the Google Maps MCP Server:
maps_geocode- Convert address to coordinatesmaps_elevation- Get elevation data for locationsmaps_distance_matrix- Calculate distances and times between points
We integrate the Google Maps Server with Analytics Middleware enabled into Cursor and ask the Agent the following imaginary scenario:
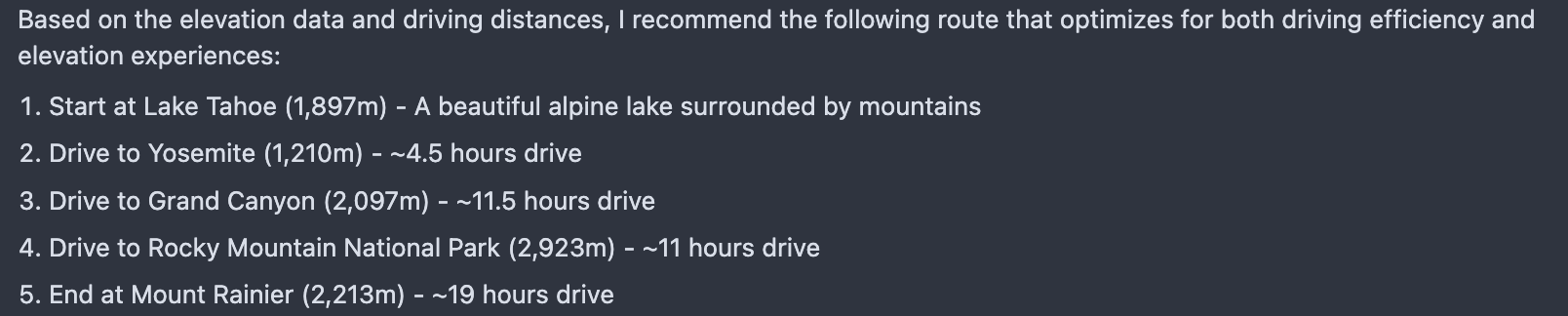
I want to visit 5 scenic nature spots in the western US for a hiking road trip. Please select from this list: Yosemite, Zion, Grand Canyon, Mount Rainier, Lake Tahoe, Rocky Mountain National Park, and Death Valley. Only pick places above 1000m elevation. Minimize total driving time and try to maximize the total elevation gain across hikes. What's the best route and why?
The LLM then starts processing the prompt and makes multiple requests to our MCP Server.
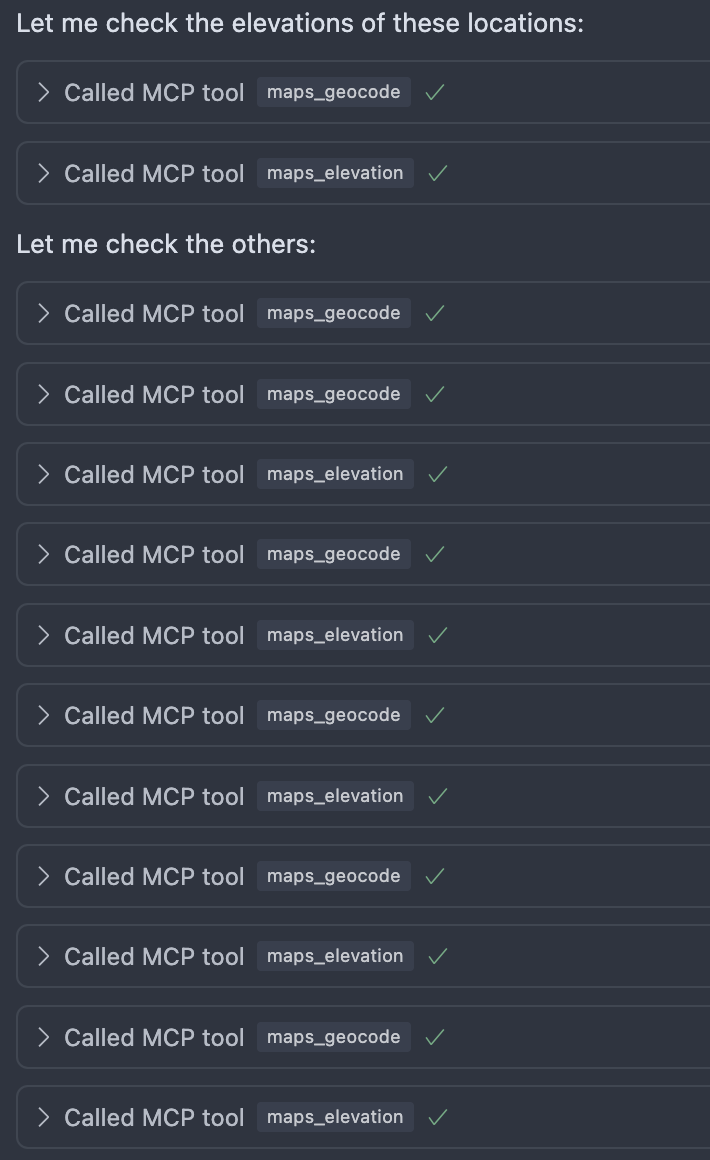
Afterwards, we can successfully see the result of the query:
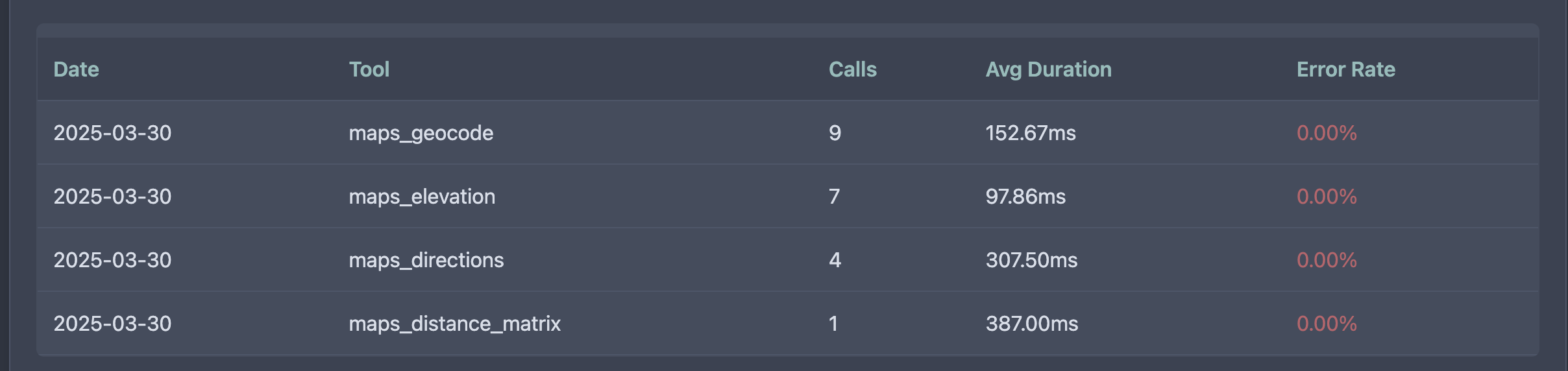
We can also open the web viewer of the analytics middleware to see statistics of all the requests using the following command:
npx -p mcp-analytics-middleware web-viewer --db-path analytics.db
Final Words
I've introduced the Model Context Protocol and its challenges and presented a small middleware tool to improve the user and developer experience. This is an early proof of concept and should be treated accordingly. Feedback is very welcome!